Hair Transplant Basics: A Complete Introduction for First-Time Patients
The concept of hair transplantation dates back several decades, but procedures have become more refined, less invasive, and more widely available in recent years. Today, many people consider it a long-term option to restore hair appearance, especially when other treatments like medications or topical solutions are ineffective.
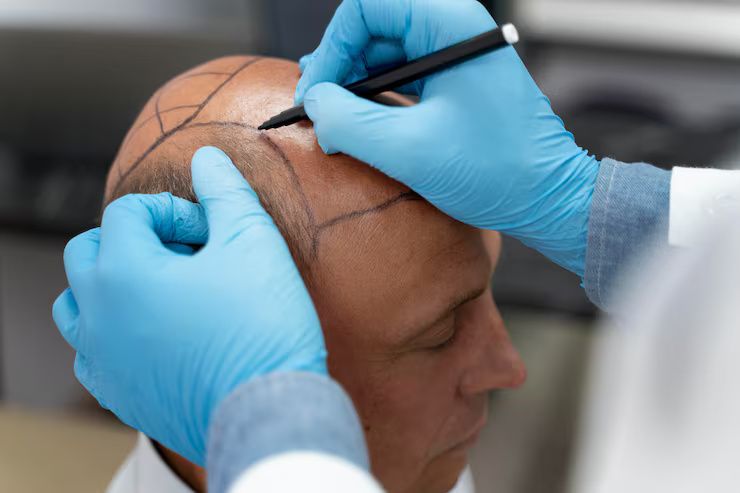
Why hair transplants matter today
Hair loss affects a large and diverse population. Causes range from genetics and aging to stress, hormonal changes, and medical conditions. While it is not physically harmful in most cases, hair loss can impact self-image, confidence, and mental well-being.
Who it affects:
-
Men with male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia)
-
Women with thinning hair or pattern baldness
-
People with hair loss from burns, surgery, or trauma
-
Cancer patients after chemotherapy (in certain cases)
-
Individuals with scalp scarring
Problems it helps address:
-
Uneven or patchy hair growth
-
Receding hairlines or bald spots
-
Loss of eyebrows, beards, or eyelashes (in specialized procedures)
-
Psychological distress due to appearance changes
Hair transplants offer a medically supervised solution that aims to redistribute existing hair in a natural-looking way. While it doesn’t create new hair, it makes better use of the hair you still have.
Recent updates and trends in hair transplantation
The field of hair restoration has seen significant updates over the past year. Key trends and innovations include:
| Trend/Update | Description |
|---|---|
| FUE advancements | Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) has become the preferred method due to minimal scarring and faster recovery. New robotic systems like ARTAS continue to improve precision (updated in early 2025). |
| Stem cell research | Ongoing trials in Japan, the US, and South Korea (as of mid-2024) are investigating stem cell therapy to regenerate hair follicles, though not yet approved for general use. |
| Unshaven FUE techniques | Growing in popularity since late 2024, this technique avoids shaving the donor area, which appeals to patients wanting a discreet approach. |
| Hair transplant tourism | Countries like Turkey, India, and Thailand remain popular for affordable hair transplants, with some clinics adopting international accreditation systems to improve quality. |
| AI in diagnosis and design | AI-powered imaging tools help map hair loss patterns and simulate expected results, improving patient consultations. Platforms like HairMetrix and TrichoLab are increasingly used in major clinics. |
These changes aim to make the process more comfortable, accessible, and personalized.
Laws and policies that regulate hair transplant procedures
Hair transplants are considered medical procedures, and regulations vary by country to ensure patient safety and professional standards. While not all countries have strict rules, the following examples highlight how legal frameworks play a role:
| Country | Regulation or Requirement | Description |
|---|---|---|
| United States | State medical board licensing | Only licensed physicians can perform or supervise hair transplants. |
| United Kingdom | Care Quality Commission (CQC) | Clinics must be registered and comply with patient safety guidelines. |
| India | Clinical Establishments Act (in many states) | Hair transplant centers must meet hygiene and safety criteria. |
| Turkey | Ministry of Health regulations | Clinics offering services to international patients must meet special accreditation standards. |
| European Union | General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Patient data from consultations must be protected under privacy rules. |
In some countries, unauthorized or unlicensed procedures can lead to serious health risks. It’s important for patients to confirm that the clinic and professionals involved meet medical and legal standards.
Tools and resources to support your decision
There are many online platforms and tools available to help first-time patients understand and plan for a hair transplant. Here are some useful resources:
Online Consultation and Simulation Tools:
-
HairMetrix – An AI tool that scans scalp condition and simulates results.
-
Bald Truth Talk Forum – Peer discussions and patient reviews.
-
RealSelf.com – Verified reviews of clinics and doctors, before-and-after galleries.
Cost Calculators and Planning Tools:
-
WhatClinic.com – Price comparisons by country and procedure.
-
Hair Transplant Cost Calculator (various clinics) – Estimate cost based on grafts needed.
-
ClinicCompare – Regional price and service comparison.
Medical Resources and Directories:
-
International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS) – Offers a global doctor directory and patient education materials.
-
British Association of Hair Restoration Surgery (BAHRS) – For patients in the UK.
Mobile Apps:
-
TrichoScan – For hair density and growth analysis.
-
Miiskin – Helps track hair thinning with regular scalp photos.
Using these resources can help patients make informed decisions, ask the right questions, and compare clinic options more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is a hair transplant permanent?
Yes, the transplanted hair is typically permanent since it’s taken from areas genetically resistant to balding. However, non-transplanted hair may continue to thin over time, so ongoing care may be needed.
2. What are the main techniques used in hair transplants?
The two primary techniques are FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) and FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction). FUE is currently more common due to less scarring and quicker recovery.
3. How long is the recovery period?
Initial recovery usually takes 7–10 days. Full results appear after 6–12 months as transplanted hair goes through natural growth cycles. Patients can usually return to work within a week.
4. Are there any risks or side effects?
Like any medical procedure, there are potential risks: swelling, infection, scarring, and temporary shedding of transplanted hairs (known as “shock loss”). Choosing a qualified practitioner reduces these risks.
5. Can women undergo hair transplants?
Yes, women with certain types of hair loss can be good candidates. However, evaluation is essential as hair thinning patterns in women differ and may not always be suitable for surgery.
Final thoughts
Hair transplants have evolved into a well-established and scientifically supported procedure for addressing hair loss. With advances in technique, technology, and safety standards, they offer a viable option for individuals looking for long-term hair restoration.
First-time patients should approach the topic with realistic expectations and thorough research. Understanding how the procedure works, recent innovations, legal considerations, and available planning tools can help ensure a safe and satisfactory experience.
